Spine Surgery Oxiplex Adhesion Barrier for Spine Surgery
At FzioMed, our barrier gel for adhesion prevention after spinal decompression and other types of spine surgery is #1 worldwide. It is available under the brand names Oxiplex®, Oxiplex/SP® Gel, Interpose® and MediShield™. 1,2
The flowable gel is supplied sterile in a 3mL syringe with a flexible applicator. It is placed at sites of tissue injury in the epidural space to serve as a temporary mechanical barrier separating opposing tissue surfaces.
Application of the adhesion barrier gel during spine surgeries; such as, lumbar laminectomy or laminotomy is simple and takes only seconds. The gel coats and isolates nerve fibers and dura, serving as a protective physical barrier that can reduce the formation of epidural fibrosis (adhesions) and can limit the exposure of nerves to biochemical irritants produced during surgery that may cause pain.
#1 Adhesion Barrier Gel
for Spine Surgery Over 600,000 units sold worldwide
Oxiplex has been available since 2002 and has been studied extensively across the world. Click here for an overview of published clinical results.
Advantages
The #1 adhesion barrier gel for spine surgery worldwide is made by FzioMed and available under the brand names Oxiplex®, Oxiplex/SP® Gel, Interpose®, and MediShield™. Made with our patented medical polymers, FzioMed adhesion barriers are the first choice of spine surgeons for protecting outcomes.
Benefits
The benefits of using a FzioMed adhesion barrier gel in spine surgery include:3
- Exceptional safety
- Designed and indicated for use in spine surgery
- Safety and performance established in spine surgery
- Ready to use
- Fast application, thorough coverage
- Colorless (to allow clear view of surgical field and neural elements)
- Absorbable
Protects the Procedure
- Separates and coats tissues
- Barrier to biochemical irritants
- Reduces adhesions
Optimizes Healing
- Moderates pain and symptoms
- Fewer adhesions
- Easier re-operations
Improves Outcomes
- Minimizes leg and back (spine) pain
- Lower re-operation rates
How it Works
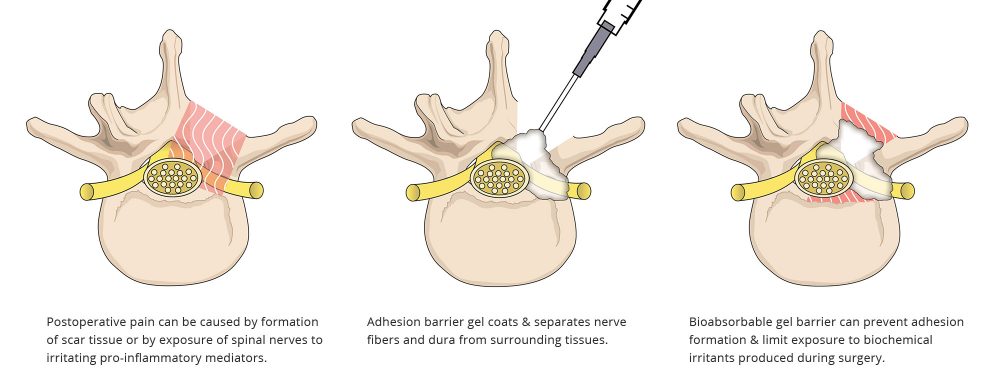
FzioMed’s adhesion barriers are designed to coat the epidural space during spinal decompression surgery, forming a temporary physical barrier as tissues heal. This protective barrier has been shown to reduce the formation of adhesions (epidural fibrosis) near the nerve root and may limit exposure of nerve tissue to irritants that can cause postoperative spine pain.
Causes of Postoperative Pain
Scar tissue known as adhesions that forms after back surgery can cause postoperative pain. Adhesions can trap and compress spinal nerves, resulting in pain even after an otherwise successful spine surgery procedure.
Postoperative pain can also be caused when sensitive spinal nerves are exposed to irritating pro-inflammatory mediators. These biochemical irritants, present in disc herniation tissue and within the epidural space, can cause sensitization of spinal nerves and surrounding tissues.
Both the formation of adhesions and the stimulation of pain mediators are part of the body’s normal response to manipulation and exposure of tissues during surgery. However, these reactions are known to be major causes of post-surgical leg and back pain, and other debilitating symptoms, that can persist long after recovery is complete.
A mainstay of postoperative pain prevention is the use of adhesion barriers, such as FzioMed’s Oxiplex®, Oxiplex/SP® Gel, Interpose® , and MediShield™ products, to coat and protect sensitive nerve tissue.
Adhesion Barriers
Adhesion barriers coat surfaces that are exposed during spinal decompression surgery, providing a temporary, protective physical barrier that isolates exposed nerve fibers and dura from surrounding tissues. These barriers function by various mechanisms:
They can prevent adhesions from forming so that the nerve is not tethered to spinal structures or compressed by epidural fibrosis.
They can limit the exposure of nerves to biochemical irritants that are produced during surgery.
Application of a FzioMed adhesion barrier gel during surgery is simple and takes only seconds. After surgery, the gel does not prevent normal healing. It is naturally cleared by the body.
Indication
Oxiplex is intended to be placed around neural tissues following spine surgery to reduce adhesion formation and related symptoms such as pain.
Clinical Experience
Please refer to the Reference Library for additional clinical resources.
Significantly Less Leg & Back Pain at 6 Months Post-Surgery 4,5,6,7,8,9
From a 352-patient US pivotal clinical study comparing lumbar surgery with Oxiplex® gel to surgery only.
Oxiplex-treated patients had 35% less leg pain and 28% less back (spine) pain at 6 months post-surgery compared to surgery-only controls (in patients with severe baseline back pain, Oxiplex n=78 vs. Controls n=78).
- Less residual leg and back pain
- Fewer neurological symptoms
- No post-op CSF leaks
- Fewer re-operations
- Enhanced patient satisfaction
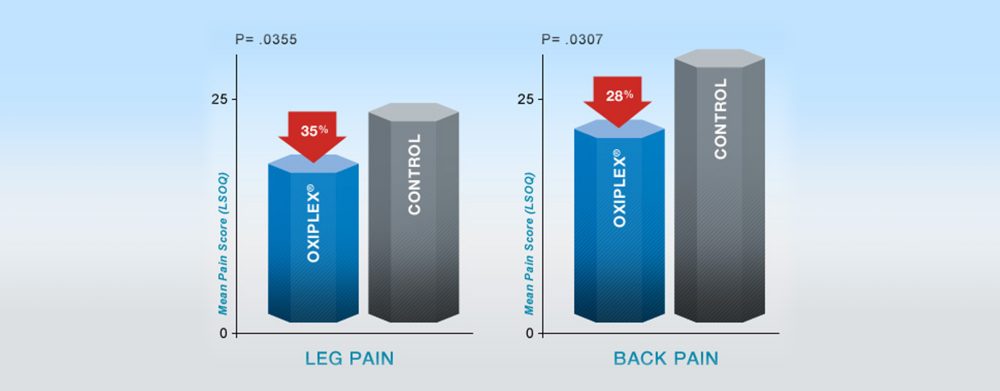
At 6 Months Post-surgery
Results shown are from a prospective, multi-center, randomized, blinded, parallel group 352-patient US pivotal clinical study comparing Oxiplex-treated patients (n=177) to surgery only (n=175), to assess the safety and effectiveness of Oxiplex spine gel to reduce postsurgical pain in patients undergoing their first single-level laminotomy, laminectomy, or discectomy at L4-L5 or L5-S1. Patients were randomly selected to receive surgery only or surgery plus Oxiplex gel placed on and around the dura and nerve root prior to wound closure. The effectiveness of Oxiplex for the reduction of pain and associated symptoms was assessed at baseline (before surgery) and at 1, 3 and 6 months following surgery using quality of life measure Lumbar Spine Outcomes Questionnaire (LSOQ) (Ben Debba et al ) and clinical evaluations.
Proportion of Subjects with Zero Leg Pain at Final Follow-up (ITT)
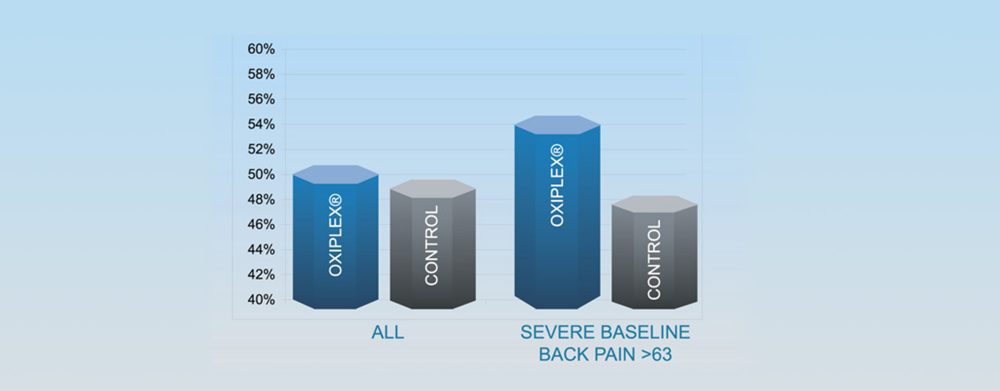
- In the severe baseline back pain group, 54.4% of Oxiplex subjects had no leg pain at final follow-up (6 months) vs. 47.5% of control subjects
- Median leg pain at 6 months in Oxiplex group was zero in both the overall ITT population and for subjects with severe baseline back pain
Responder Analysis Overall Treatment Success at 6 Months
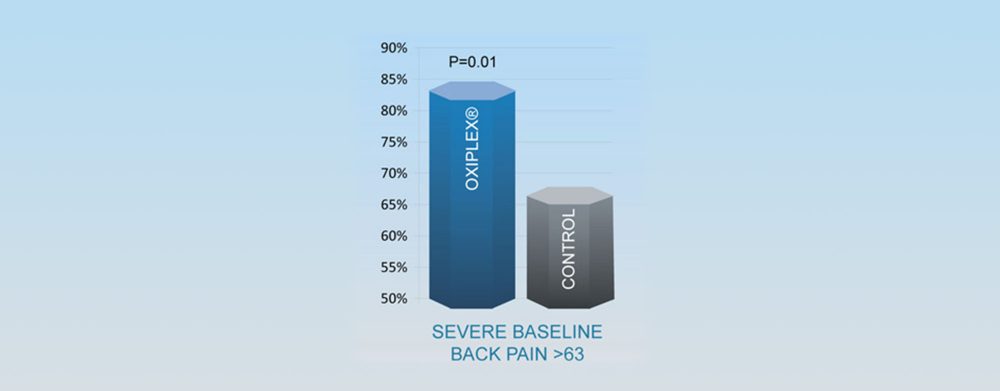
Responder Analysis Definition
- Reduction of at least 20 points in LSOQ composite score
- No additional procedures on lower back
- Absence of neurological deficits
Fewer Re-Operations in Oxiplex-Treated Patients
Patients in the Oxiplex group had fewer re-operations during the 6-month follow-up period than patients in the surgery-only Control group:
Excellent Safety Record Over 600,000 patients treated
Oxiplex is intended to be placed around neural tissues following spine surgery to reduce adhesion formation and related symptoms such as pain.
Safety Profile and Performance
In the prospective, multi-center, randomized, controlled, third-party blinded 352-patient U.S. pivotal clinical trial comparing Oxiplex-treated patients (n=177) to surgery only (n=175), to assess the safety and effectiveness of Oxiplex spine gel to reduce postsurgical pain and symptoms in patients undergoing single-level laminotomy, laminectomy, or discectomy at L4-L5 or L5-S1.
In all study patients (Oxiplex N=177, Controls N=175) there were:
- No significant difference in adverse events and serious adverse events between Oxiplex and Control groups. No adverse events led to discontinuation of any subject or discontinuation of the study.
- No serious adverse events related to Oxiplex.
- Fewer neurological abnormalities in Oxiplex group compared to Control group.
- Fewer musculoskeletal abnormalities in Oxiplex group compared to Control group.
- Fewer reoperations in Oxiplex group compared to Control group (1 vs. 6).
In independent studies, excellent safety related to the use of CMC/PEO spine gels. 10, 11, 12, 13
In pre-clinical studies, reduction of epidural fibrosis was accompanied by normal bone healing and CMC/PEO gels did not inhibit dural healing.14, 15
Evidence-based performance summary on FzioMed’s adhesion barrier gel for lumbar spine surgery (available under the brand names Oxiplex®, Oxiplex/SP® Gel and MediShield™). Information provided is summarized from published literature or presentations. Refer to citations for complete data.
Performance Summary
Evidence for reduction of leg and back pain5,6,7,8
Indication for Surgery:
- Laminectomy, laminotomy, discectomy (352 patients)
Method / Material:
- 352-patient multi-center, randomized, controlled, blinded U.S. pivotal trial. Surgery for unilateral herniation of lumbar disc at L4-L5 or L5-S1. Patients treated with surgery plus Oxiplex gel (N=177) or surgery alone (N=175).
Results / Conclusion:
- Patients with severe baseline back pain treated with surgery plus Oxiplex gel had a statistically significant reduction in leg and back pain at six months post-surgery compared to controls (Oxiplex n=78 vs Controls n=78).
Evidence for safety10
Indication for Surgery:
- Lumbar discectomy (396 patients)
Method / Material:
- 396 patients treated with Oxiplex gel over a 3-year period (January 2003 thru December 2005) were evaluated for side effects such as skin reactions, general reactions, and reoperations.
Results / Conclusion:
- No product related complications were observed. In five patients needing reoperations for recurrent herniation, significant but subjective reduction in fibrosis was observed at second surgery. Gel was well tolerated as an agent to achieve reduction of fibrosis in lumbar disc surgery.
Evidence for reduction of leg pain and disability scores13
Indication for Surgery:
- Posterior lumbar microdiscectomy for disc herniation (70 patients)
Method / Material:
- Consecutive series of 70 patients undergoing surgery for unilateral herniation of lumbar disc at L3-L4, L4-L5, or L5-S1 treated with CMC/PEO gel (n=35) or without gel (n=35). Patients assessed before surgery and regularly over three years post-surgery, for disability using Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) and for leg and back using Visual Analog Scale (VAS).
Results / Conclusion:
- In a 3-year follow-up, CMC/PEO gel significantly reduced disability and leg pain scores compared with conventional treatment (no gel). CMC/PEO gel was found to be safe to use, easy to apply and required minimal additional surgical time.
Evidence for reduction of epidural fibrosis in lumbar surgery with normal bone healing14
Indications:
- Laminotomy and laminectomy model (rabbit)
Method / Material:
- Two laminotomy or laminectomy sites per animal at L4 and L6. Sites treated with compositions of CMC/PEO gels or films and compared to control sites (no gel).
Results / Conclusion:
- Direct visualization and histological evaluations showed CMC/PEO compositions reduced frequency and extent of epidural fibrosis compared to controls (no gel). Reduction of epidural fibrosis was accompanied by normal bone healing.
Evidence for effect on dural healing15
Indications:
- Two-level laminectomy and epidural fibrosis model (rabbit)
Method / Material:
- Two-level laminectomy performed at L4 and L5 in three groups of rabbits; FzioMed CMC/PEO gel group (n=35), Adcon-L group (n=28) and no gel control group (n=34).
Results / Conclusion:
- Gross and histological evaluations showed that application of CMC/PEO gel significantly reduced formation of epidural fibrosis but did not inhibit healing of dural incisions.
Evidence for reduction of radiculopathy in spinal surgery16
Indications:
- One-level microdiscectomy (270 patients)
Method / Material:
- Three groups of patients treated with MediShield Anti-adhesion Gel (n=90), Adcon-L gel (n=90) and no gel (n=90) and results compared at 6 weeks post-surgery.
Results / Conclusion:
- MediShield gel patient group had a greater reduction in residual radiculopathy and need for physiotherapy compared to other groups. In recurrent cases, MediShield Anti-adhesion Gel reduced adhesion formation thereby shortening surgery time and reducing risk of damaging nerve root.
Instructions for Use
Click here to request the most recent revision of this product’s instructions for use. Please state the product name for the IFU requested in the comments section.
Availability
FzioMed offers innovative adhesion barrier products such as Oxiplex®, Oxiplex/SP® Gel, Interpose®, MediShield™, Oxiplex/AP®, and DYNAVISC®. These products are designed for use by medical professionals. Click here to contact FzioMed for more information on product availability in your country.
Last Updated: March 14, 2023
